Identifiers and Description
Identifiers and Description
Gene Model Identifier
TTHERM_00660180Standard Name
HMGB1 (High MoBility group 1)Aliases
PreTt23762 | 98.m00105 | 3736.m00006 | HMGBDescription
HMGB high mobility group (HMG) box protein; High-Mobility-Group (HMG) protein; induces negative supercoiling of DNA in vitro; present in both macro- and micronuclei but with elevated expression during both macronuclear S phase and endoreplication of developing new macronucleiGenome Browser (Macronucleus)
Genome Browser (Micronucleus)
 External Links
External Links
 Gene Ontology Annotations
Gene Ontology Annotations
Cellular Component
- macronucleus (IDA) | GO:0031039
- micronucleus (IDA) | GO:0031040
- nucleus (IEA) | GO:0005634
Molecular Function
- DNA binding (IDA) | GO:0003677
- DNA binding (IEA) | GO:0003677
- DNA topoisomerase activity (IDA) | GO:0003916
Biological Process
- conjugation with mutual genetic exchange (IEP) | GO:0000748
 Domains
Domains
- ( PF00505 ) HMG (high mobility group) box
 Gene Expression Profile
Gene Expression Profile
 Vegetative Cell Cycle (Zhang et al.,
2023)
Vegetative Cell Cycle (Zhang et al.,
2023)
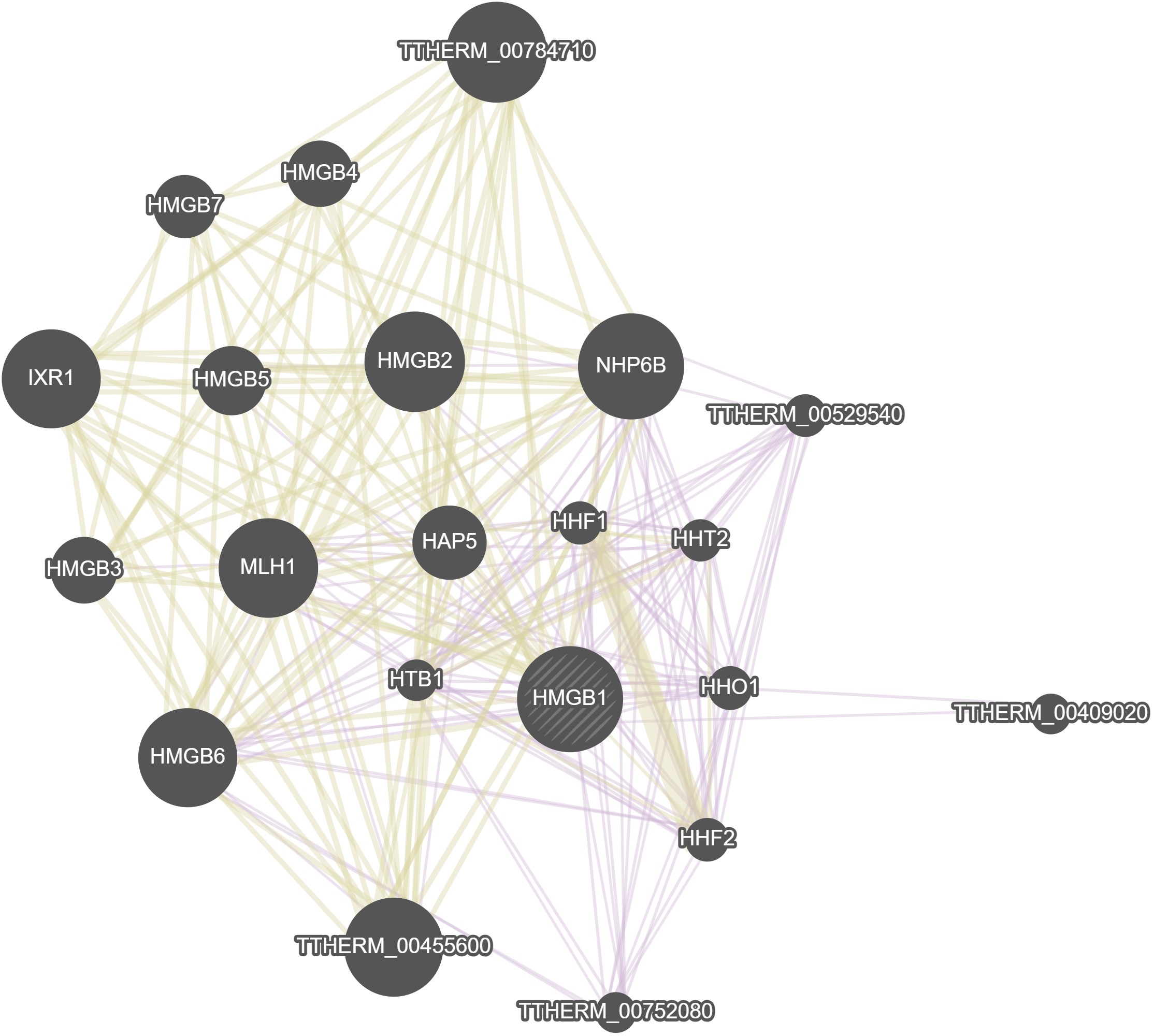
 GeneMania
GeneMania
 Tetrahymena Stock Center
Tetrahymena Stock Center
 Homologs
Homologs
Source Identifier Score Tetrahymena borealis EI9_17254.1 5.001636743996964e-56 Description: HMG box family protein (147 aa) SGD YDR174W 0.000006997203421143941 Description: HMO1 Chromatin associated high mobility group (HMG) family member involved in genome maintenance; rDNA-binding component of the Pol I transcription system; associates with a 5-3 DNA helicase and Fpr1p, a prolyl isomerase WormBase WBGene00022182 0.0000899730839127287 Description: locus:swsn-3 status:Confirmed UniProt:Q9BL39 protein_id:CCD73870.1 Oxytricha Contig12963.0.1.g3 0.00010003404299092957 Description: HMG (high mobility group) box Stentor Coeruleus SteCoe_14619 0.0024787521766663585 Description: None
 General Information
General Information
No Data fetched for General Information
 Associated Literature
Associated Literature
- Ref:31932604: Nabeel-Shah S, Ashraf K, Saettone A, Garg J, Derynck J, Lambert JP, Pearlman RE, Fillingham J (2020) Nucleus-specific linker histones Hho1 and Mlh1 form distinct protein interactions during growth, starvation and development in Tetrahymena thermophila. Scientific reports 10(1):168
- Ref:8264578: Wu M, Allis CD, Sweet MT, Cook RG, Thatcher TH, Gorovsky MA (1994) Four distinct and unusual linker proteins in a mitotically dividing nucleus are derived from a 71-kilodalton polyprotein, lack p34cdc2 sites, and contain protein kinase A sites. Molecular and cellular biology 14(1):10-20
- Ref:8417323: Wang T, Allis CD (1993) An abundant high-mobility-group-like protein is targeted to micronuclei in a cell cycle-dependent and developmentally regulated fashion in Tetrahymena thermophila. Molecular and cellular biology 13(1):163-73
- Ref:1589033: Lilley DM (1992) DNA--protein interactions. HMG has DNA wrapped up. Nature 357(6376):282-3
- Ref:1480473: Wang T, Allis CD (1992) Replication-dependent and independent regulation of HMG expression during the cell cycle and conjugation in Tetrahymena. Nucleic acids research 20(24):6525-33
- Ref:1991550: Schulman IG, Wang TT, Stargell LA, Gorovsky MA, Allis CD (1991) Cell-cell interactions trigger the rapid induction of a specific high mobility group-like protein during early stages of conjugation in Tetrahymena. Developmental biology 143(2):248-57
- Ref:1986218: Schulman IG, Wang T, Wu M, Bowen J, Cook RG, Gorovsky MA, Allis CD (1991) Macronuclei and micronuclei in Tetrahymena thermophila contain high-mobility-group-like chromosomal proteins containing a highly conserved eleven-amino-acid putative DNA-binding sequence. Molecular and cellular biology 11(1):166-74
- Ref:2514183: Suda M, Hayashi H (1989) A protein that accumulates during starvation in Tetrahymena nuclei. Journal of biochemistry 106(4):612-5
- Ref:2760016: Hayashi T, Hayashi H, Iwai K (1989) Tetrahymena HMG nonhistone chromosomal protein. Isolation and amino acid sequence lacking the N- and C-terminal domains of vertebrate HMG 1. Journal of biochemistry 105(4):577-81
- Ref:2476991: Hamana K, Kawada K (1989) Release of nucleosomes from nuclei by bleomycin-induced DNA strand scission. Biochemistry international 18(5):971-9
- Ref:3584238: Schulman IG, Cook RG, Richman R, Allis CD (1987) Tetrahymena contain two distinct and unusual high mobility group (HMG)-like proteins. The Journal of cell biology 104(6):1485-94
- Ref:3109974: Prasanna P, Holmlund CE (1987) Identification in Tetrahymena pyriformis of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme a lyase: its purification and properties. The International journal of biochemistry 19(4):385-9
- Ref:3671074: Roth SY, Schulman IG, Cook RG, Allis CD (1987) The complete amino acid sequence of an HMG-like protein isolated from the macronucleus of Tetrahymena. Nucleic acids research 15(19):8112
- Ref:6849878: Levy-Wilson B, Denker MS, Ito E (1983) Isolation, characterization, and postsynthetic modifications of tetrahymena high mobility group proteins. Biochemistry 22(7):1715-21
- Ref:6258140: Hamana K, Zama M (1980) Selective release of HMG nonhistone proteins during DNase digestion of Tetrahymena chromatin at different stages of the cell cycle. Nucleic acids research 8(22):5275-88
- Ref:117005: Hamana K, Iwai K (1979) High mobility group nonhistone chromosomal proteins also exist in Tetrahymena. Journal of biochemistry 86(3):789-94
 Sequences
Sequences
>TTHERM_00660180(coding)
ATGTCTAAAGCTGCTAGCCAATACGCAACTCTCGAAGATCTCCCCTCCAAGCCCAAGAGA
CCCCAAACCGGTTTCTTCATCTACAAGAGTGAAGTCTTTGCCAAGAGAAGAACTGAGTGC
CCCAACTTGAAGGTCCCTGAAATCGTCTCTAAAATTAGTGAAGAATACAAGGCCTTACCT
GAAAAGGAGAAGTAAAAATACGAAGAAGCCTACAGAAAGGAAAAGGCCACCTACGATAAG
TAAAACGACCAATGGAAAGAGAAGTATGGTGATATCGAAAAGTCCTTGAAGGATTAGGCT
AAGAAGGCCCTCAAGGAAAAGACCAAAAAGTCCAAGGCTGCTGAAAAGGAACTTGAAAAG
AGCAAGAAGAAGGCTCCCGCTGCTGCCCCTGCCAAGAAGGACGATAAGAAGGCTCCCGCT
AAGAAGAAATGA>TTHERM_00660180(gene)
ATGTCTAAAGCTGCTAGCCAATACGCAACTCTCGAAGATCTCCCCTCCAAGCCCAAGAGA
CCCCAAACCGGTTTCTTCATCTACAAGAGTGAAGTCTTTGCCAAGAGAAGAACTGAGTGC
CCCAACTTGAAGGTCCCTGAAATCGTCTCTAAAATTAGTGAAGAATACAAGGCCTTACCT
GAAAAGGAGAAGTAAAAATACGAAGAAGCCTACAGAAAGGAAAAGGCCACCTACGATAAG
TAAAACGACCAATGGAAAGAGAAGTATGGTGATATCGAAAAGTCCTTGAAGGATTAGGCT
AAGAAGGCCCTCAAGGAAAAGACCAAAAAGTCCAAGGCTGCTGAAAAGGAACTTGAAAAG
AGCAAGAAGAAGGCTCCCGCTGCTGCCCCTGCCAAGAAGGACGATAAGAAGGCTCCCGCT
AAGAAGAAATGA>TTHERM_00660180(protein)
MSKAASQYATLEDLPSKPKRPQTGFFIYKSEVFAKRRTECPNLKVPEIVSKISEEYKALP
EKEKQKYEEAYRKEKATYDKQNDQWKEKYGDIEKSLKDQAKKALKEKTKKSKAAEKELEK
SKKKAPAAAPAKKDDKKAPAKKK