Identifiers and Description
Identifiers and Description
Gene Model Identifier
TTHERM_00143660Standard Name
HTA3 (Histone h Two A 3 )Aliases
histone H2A var hv1 | hv1 | H2A.Z | PreTt26673 | 11.m00370 | 3702.m00093Description
HTA3 histone H2A; Histone H2A (variant H2A.Z); essential protein; regulated by acetylation, which modulates charge patch on its N-terminal tail; comprises about 20% of total H2A protein in Tetrahymena; found only in transcriptionally active nuclei; Histone H2AGenome Browser (Macronucleus)
Genome Browser (Micronucleus)
 External Links
External Links
 Gene Ontology Annotations
Gene Ontology Annotations
Cellular Component
- macronucleus (IDA) | GO:0031039
- micronucleus (TAS) | GO:0031040
- subrhabdomeral cisterna (IEA) | GO:0016029
Molecular Function
- 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone binding (IEA) | GO:1903880
- 2-keto-3-deoxy-L-rhamnonate aldolase activity (IEA) | GO:0106099
- DNA binding (ISS) | GO:0003677
- ferric enterobactin:proton symporter activity (IEA) | GO:0015345
- lanosterol synthase activity (IEA) | GO:0000250
- mitochondrial single subunit type RNA polymerase activity (IEA) | GO:0001065
- obsolete sodium-transporting two-sector ATPase activity (IEA) | GO:0015443
- obsolete zinc, iron permease activity (IEA) | GO:0015342
- phosphatidylserine decarboxylase activity (IEA) | GO:0004609
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (ATP) activity (IEA) | GO:0004612
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity (IEA) | GO:0004611
- siderophore-iron transmembrane transporter activity (IEA) | GO:0015343
- type 4 neuropeptide Y receptor binding (IEA) | GO:0031844
Biological Process
- cellular response to homocysteine (IEA) | GO:1905375
- coenzyme A biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0015937
- heme A biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006784
- heme biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006783
- inactivation of recombination (HML) (IEA) | GO:0007537
- induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals (IEA) | GO:0008624
- lung connective tissue development (IEA) | GO:0060427
- lung epithelium development (IEA) | GO:0060428
- lung saccule development (IEA) | GO:0060430
- negative regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902647
- negative regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902642
- negative regulation of cellular glucuronidation (IEA) | GO:2001030
- negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response (IEA) | GO:1903898
- neutral lipid metabolic process (IEA) | GO:0006638
- obsolete aging (IEA) | GO:0007568
- obsolete extracellular carbohydrate transport (IEA) | GO:0006859
- obsolete regulation of histone H3-K27 methylation (IEA) | GO:0061085
- ommochrome biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006727
- plant-type cell wall modification (IEA) | GO:0009827
- positive regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902643
- positive regulation of dendrite extension (IEA) | GO:1903861
- positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription (IEP) | GO:0045893
- positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining (IEA) | GO:2001034
- positive regulation of oxidative phosphorylation (IEA) | GO:1903862
- positive regulation of phospholipid translocation (IEA) | GO:0061092
- primary lung bud formation (IEA) | GO:0060431
- propan-2-ol biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902640
- protein localization to old growing cell tip (IEA) | GO:1903858
- pyrimidine nucleotide salvage (IEA) | GO:0032262
- regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902646
- regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902641
- regulation of cytokinin dehydrogenase activity (IEA) | GO:1903856
- regulation of ecdysteroid secretion (IEA) | GO:0007555
- regulation of gastric motility (IEA) | GO:1905333
- regulation of phosphorus utilization (IEA) | GO:0006795
- regulation of plant epidermal cell differentiation (IEA) | GO:1903888
- regulation of RNA binding transcription factor activity (IEA) | GO:1905255
- sesquiterpenoid biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0016106
- sperm aster formation (IEA) | GO:0035044
- sperm DNA decondensation (IEA) | GO:0035041
- synaptic vesicle priming (IEA) | GO:0016082
- tertiary alcohol biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902645
- transcription by RNA polymerase V (IEA) | GO:0001060
- tRNA import into mitochondrion (IEA) | GO:0016031
 Domains
Domains
 Gene Expression Profile
Gene Expression Profile
 Vegetative Cell Cycle (Zhang et al.,
2023)
Vegetative Cell Cycle (Zhang et al.,
2023)
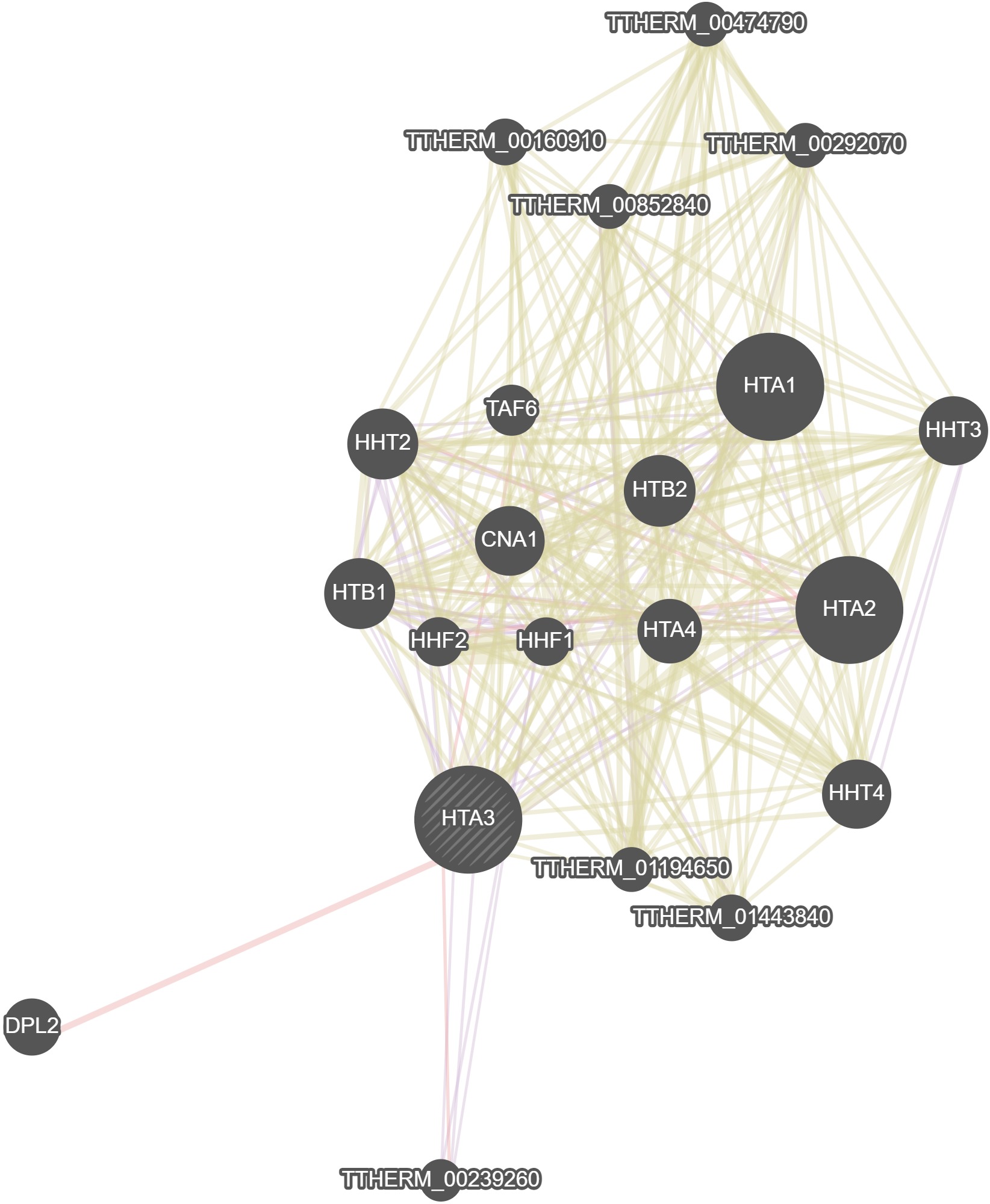
 GeneMania
GeneMania
 Tetrahymena Stock Center
Tetrahymena Stock Center
- ( SD02070 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutations K4R,K7R,K10R,K13R, K21R.
- ( SD02071 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutations K4R,K7R,K10R,K16R, K21R.
- ( SD02072 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutations Del4-24 aa.
- ( SD02073 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutations K4Q,K7Q,K10Q,K13Q,K16Q,K21R
- ( SD02074 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutations K4Q,K7R,K10Q,K13Q,K16Q,K21Q
- ( SD02075 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutations K7R,K10R,K13R,K16R,K21R
- ( SD02076 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutations K4R,K10R,K13R,K16R,K21R
- ( SD02454 ) Macronucleus: GFP tagged HTAZ
- ( SD02455 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutations K4Q,K7R,K10Q,K13Q,K16Q,K21Q
- ( SD02456 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutations K4R, K7R,K10R,K13R,K16R.
- ( SD02457 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutation K130R
- ( SD02458 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutation K130R
- ( SD02462 ) Macronucleus: inserted HTAZ with K4R Into MTT1 locus and neo2 in 5’ flanking of MTT1
- ( SD02463 ) Macronucleus: inserted HTAZ with K4R,K7R,K10R,K13R K16R, K21R Into MTT1 locus and neo2 in 5’ flanking of MTT1
- ( SD02464 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding replaced with mutations K4R, K7R,K10R,K13R,K16R,K21R,K23Q, K24Q
- ( SD02465 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: H2A.Z with a major H2A.1 n-terminal tail, S1V and 5R mutations.
- ( SD02672 ) Micronucleus: neo2 into HTAZ coding
- ( SD02673 ) Micronucleus: neo2 into HTAZ coding
- ( SD02674 ) Micronucleus: neo2 into HTAZ coding
- ( SD02675 ) Micronucleus: neo2 into HTAZ coding
- ( SD02684 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding
- ( SD02685 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding,
- ( SD02686 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding
- ( SD02687 ) Micronucleus: Neo2 in HTAZ Macronucleus: HTAZ coding
- ( SD02688 ) Micronucleus: neo2 replaces HTAZ coding Macronucleus: HTAZ coding either neo2 or mutated to K130R
- ( SD02689 ) Micronucleus: neo2 replaces HTAZ coding Macronucleus: HTAZ coding either neo2 or mutated to K130R
- ( SD02690 ) Micronucleus: neo2 replaces HTAZ coding Macronucleus: HTAZ coding either neo2 or mutated to K130R
- ( SD02691 ) Micronucleus: neo2 replaces HTAZ coding Macronucleus: HTAZ coding either neo2 or mutated to K130R
- ( SD02874 ) Macronucleus: neo2 into HTA3
- ( SD02875 ) Macronucleus: neo2 into HTA3
 Homologs
Homologs
No Data fetched for Homologs
 General Information
General Information
No Data fetched for General Information
 Associated Literature
Associated Literature
- Ref:30796450: Ashraf K, Nabeel-Shah S, Garg J, Saettone A, Derynck J, Gingras AC, Lambert JP, Pearlman RE, Fillingham J (2019) Proteomic analysis of histones H2A/H2B and variant Hv1 in Tetrahymena thermophila reveals an ancient network of chaperones. Molecular biology and evolution ( ):
- Ref:12665578: Ren Q, Gorovsky MA (2003) The nonessential H2A N-terminal tail can function as an essential charge patch on the H2A.Z variant N-terminal tail. Molecular and cellular biology 23(8):2778-89
- Ref:11430834: Ren Q, Gorovsky MA (2001) Histone H2A.Z acetylation modulates an essential charge patch. Molecular cell 7(6):1329-35
- Ref:8754831: Liu X, Li B, GorovskyMA (1996) Essential and nonessential histone H2A variants in Tetrahymena thermophila. Molecular and cellular biology 16(8):4305-11
- Ref:8276246: Stargell LA, Bowen J, Dadd CA, Dedon PC, Davis M, Cook RG, Allis CD, Gorovsky MA (1993) Temporal and spatial association of histone H2A variant hv1 with transcriptionally competent chromatin during nuclear development in Tetrahymena thermophila. Genes & development 7(12B):2641-51
- Ref:3211129: White EM, Gorovsky MA (1988) Localization and expression of mRNA for a macronuclear-specific histone H2A variant (hv1) during the cell cycle and conjugation of Tetrahymena thermophila. Molecular and cellular biology 8(11):4780-6
- Ref:3340523: White EM, Shapiro DL, Allis CD, Gorovsky MA (1988) Sequence and properties of the message encoding Tetrahymena hv1, a highly evolutionarily conserved histone H2A variant that is associated with active genes. Nucleic acids research 16(1):179-98
- Ref:3944120: Allis CD, Richman R, Gorovsky MA, Ziegler YS, Touchstone B, Bradley WA, Cook RG (1986) hv1 is an evolutionarily conserved H2A variant that is preferentially associated with active genes. The Journal of biological chemistry 261(4):1941-8
- Ref:6692982: Allis CD, Wiggins JC (1984) Histone rearrangements accompany nuclear differentiation and dedifferentiation in Tetrahymena. Developmental biology 101(2):282-94
- Ref:6373790: Wenkert D, Allis CD (1984) Timing of the appearance of macronuclear-specific histone variant hv1 and gene expression in developing new macronuclei of Tetrahymena thermophila. The Journal of cell biology 98(6):2107-17
 Sequences
Sequences
>TTHERM_00143660(coding)
ATGGCTGGCGGAAAAGGCGGTAAAGGTGGTAAAGGTGGCAAAGGTGGTAAAGTCGGAGGC
GCCAAGAATAAGAAGACTCCTCAATCACGTTCTTATAAGGCTGGTTTATAATTCCCAGTC
GGTAGAATCCACAGATTTTTGAAGGGTAGAGTTAGTGCTAAGAACAGAGTTGGTGCTACT
GCTGCTGTTTATGCTGCTGCTATTTTGGAATATTTAACAGCAGAAGTTTTGGAATTGGCT
GGTAATGCTTCTAAGGATTTCAAAGTCAGAAGAATCACTCCTCGTCACTTGCTCTTGGCT
ATTAGAGGTGATGAAGAATTAGATATTTTGATCAAGGCTACCATTGCTGGTGGTGGTGTC
ATTCCTCACATCCATAAAGCTCTCTTGGGTAAGCACTCTACTAAAAACAGATCTAGTGCT
AAGACTGCTGAACCTCGTTGA>TTHERM_00143660(gene)
CAAAAAAAGAAAAATTAAAAGAAAAAGAAATAAAAACAAGTAAAAAAGAAAATGGCTGGC
GGAAAAGGCGGTAAAGGTGGTAAAGGTGGCAAAGGTGGTAAAGTCGGAGGCGCCAAGAAT
AAGAAGACTCCTCAATCACGTTCTTATAAGGCTGGTTTATAATTCCCAGTCGGTAGAATC
CACAGATTTTTGAAGGGTAGAGTTAGTGCTAAGAACAGAGTTGGTGCTACTGCTGCTGTT
TATGCTGCTGCTATTTTGGAATATTTAACAGCAGAAGTTTTGGAATTGGCTGGTAATGCT
TCTAAGGATTTCAAAGTCAGAAGAATCACTCCTCGTCACTTGCTCTTGGCTATTAGAGGT
GATGAAGAATTAGATATTTTGATCAAGGCTACCATTGCTGGTGGTGGTGTCATTCCTCAC
ATCCATAAAGCTCTCTTGGGTAAGCACTCTACTAAAAACAGATCTAGTGCTAAGACTGCT
GAACCTCGTTGAGTAGTAATGTACATGATTTAAAAAAAAATTACAAAACAACTCAATAAA
ATTCAATATTATAATAATTCAACCTATATATATATTATTACTATGCTGACTGGTTCACGG
ATGGAGGAAGGAAAAGCAGTACTGCGCTCATAGCATAAATATTTTTGGAAATTCTCTCAA
ATACTTTTATCAACCTCAACATGAAATAATAATTAACACTGTAAAAATACAAAAAATCTA
TAAATTCTCCTACTTCTAAAAGATTGTTCTCAACACCTAAAGCTCATTTAGGATTACTAT
CTTCAGATTCTGCAAGCTCTAAGGACAACTCGCAATTTTCCAAAGAATGGTATCCTTTTG
CGCAGCAGGATAGAAGTTATTGAGTAAAAAAATTACAAAAATGTATATGTATTTGTGTAT
GTGCTATTTCAATGTACTTTCTTCTTACTAGTTCAATAATATGTGTTTGATTAAAGTAGA
GTATGTGTATTAAGGA>TTHERM_00143660(protein)
MAGGKGGKGGKGGKGGKVGGAKNKKTPQSRSYKAGLQFPVGRIHRFLKGRVSAKNRVGAT
AAVYAAAILEYLTAEVLELAGNASKDFKVRRITPRHLLLAIRGDEELDILIKATIAGGGV
IPHIHKALLGKHSTKNRSSAKTAEPR