Identifiers and Description
Identifiers and Description
Gene Model Identifier
TTHERM_00189170Standard Name
HHF2 (Histone H Four 2)Aliases
histone H4-II gene | 15.m00378 | PreTt08667 | 3697.m00090Description
HHF2 histone H4; Histone H4; one of the four histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) that comprise the protein core of the eukaryotic nucleosome; adjacent to HHT2; encoded protein identical to Hhf1p; expressed during macronuclear and micronuclear S-phase; CENP-T/Histone H4, histone foldGenome Browser (Macronucleus)
Genome Browser (Micronucleus)
 External Links
External Links
 Gene Ontology Annotations
Gene Ontology Annotations
Cellular Component
- macronucleus (TAS) | GO:0031039
- micronucleus (TAS) | GO:0031040
- nuclear nucleosome (ISS) | GO:0000788
- prospore membrane spindle pole body attachment site (IEA) | GO:0070057
Molecular Function
- 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone binding (IEA) | GO:1903880
- deUFMylase activity (IEA) | GO:0071567
- lanosterol synthase activity (IEA) | GO:0000250
- mitochondrial single subunit type RNA polymerase activity (IEA) | GO:0001065
- obsolete bacterial-type RNA polymerase activity (IEA) | GO:0001061
- obsolete plastid PEP-B RNA polymerase activity (IEA) | GO:0001063
- obsolete sodium-transporting two-sector ATPase activity (IEA) | GO:0015443
- phosphatidylserine decarboxylase activity (IEA) | GO:0004609
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (ATP) activity (IEA) | GO:0004612
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity (IEA) | GO:0004611
- plastid single-subunit type RNA polymerase binding (IEA) | GO:0001051
- single-subunit type RNA polymerase binding (IEA) | GO:0001050
- type 4 neuropeptide Y receptor binding (IEA) | GO:0031844
- UFM1 transferase activity (IEA) | GO:0071568
Biological Process
- 3-keto-sphinganine metabolic process (IEA) | GO:0006666
- cellular response to dopamine (IEA) | GO:1903351
- chromatin assembly or disassembly (ISS) | GO:0006333
- commissural neuron axon guidance (IEA) | GO:0071679
- heme A biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006784
- heme biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006783
- induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals (IEA) | GO:0008624
- negative regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902647
- negative regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902642
- negative regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway (IEA) | GO:0070100
- negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response (IEA) | GO:1903898
- neutral lipid metabolic process (IEA) | GO:0006638
- nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway (IEA) | GO:0070431
- obsolete extracellular carbohydrate transport (IEA) | GO:0006859
- obsolete mRNA endonucleolytic cleavage involved in unfolded protein response (IEA) | GO:0070055
- obsolete regulation of histone H3-K27 methylation (IEA) | GO:0061085
- obsolete regulation of nucleic acid-templated transcription (IEA) | GO:1903506
- obsolete response to long exposure to lithium ion (IEA) | GO:0043460
- ommochrome biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006727
- photosynthetic NADP+ reduction (IEA) | GO:0009780
- plant-type cell wall modification (IEA) | GO:0009827
- positive regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902643
- positive regulation of dendrite extension (IEA) | GO:1903861
- positive regulation of oxidative phosphorylation (IEA) | GO:1903862
- positive regulation of phospholipid translocation (IEA) | GO:0061092
- positive regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1901800
- propan-2-ol biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902640
- protein localization to medial cortex (IEA) | GO:0071574
- protein localization to old growing cell tip (IEA) | GO:1903858
- regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902646
- regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902641
- regulation of bile acid metabolic process (IEA) | GO:1904251
- regulation of cytokinin dehydrogenase activity (IEA) | GO:1903856
- regulation of phosphorus utilization (IEA) | GO:0006795
- regulation of plant epidermal cell differentiation (IEA) | GO:1903888
- striated muscle myosin thick filament assembly (IEA) | GO:0071688
- tertiary alcohol biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902645
- transcription by RNA polymerase V (IEA) | GO:0001060
 Domains
Domains
- ( PF15511 ) Centromere kinetochore component CENP-T histone fold
 Gene Expression Profile
Gene Expression Profile
 Vegetative Cell Cycle (Zhang et al.,
2023)
Vegetative Cell Cycle (Zhang et al.,
2023)
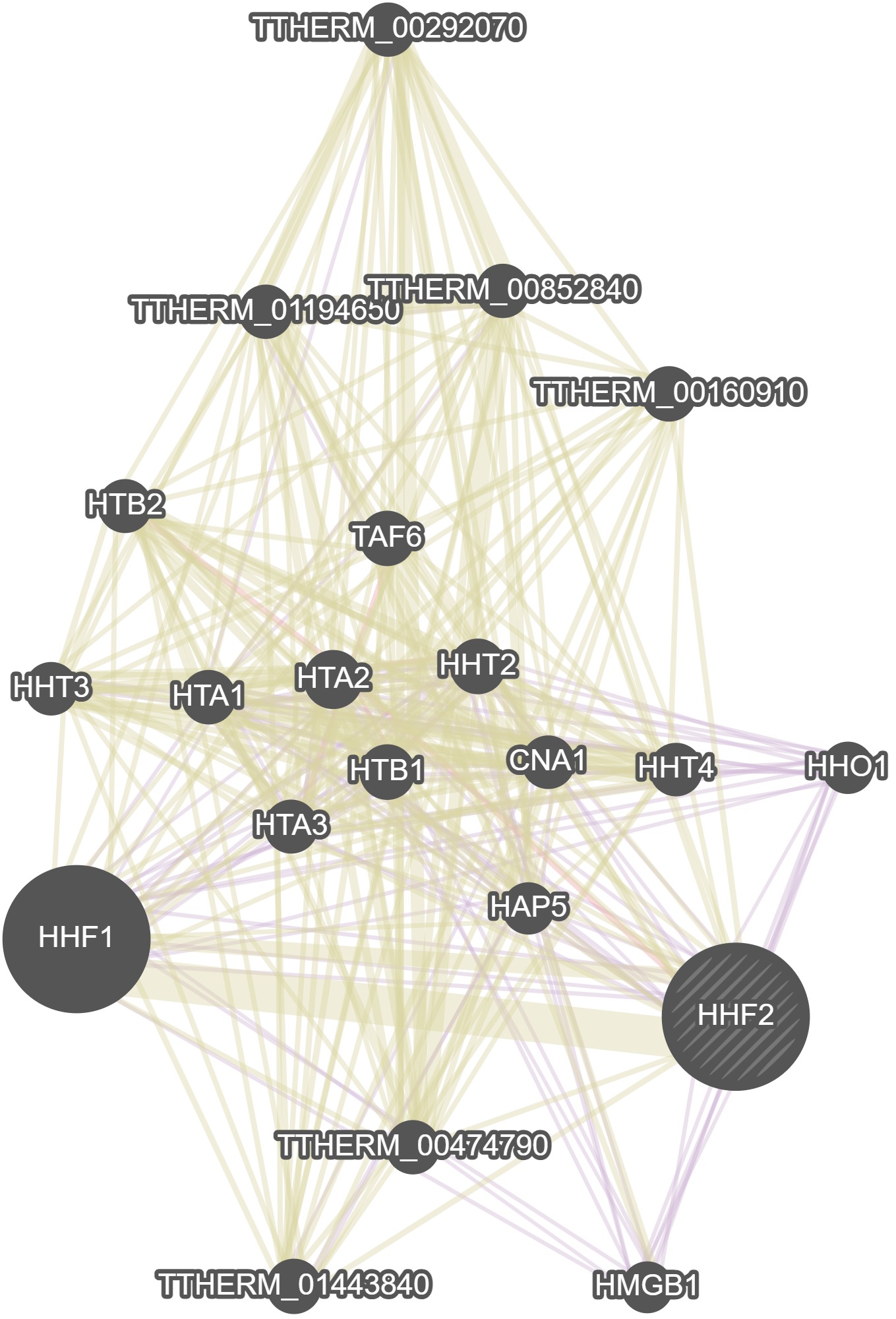
 GeneMania
GeneMania
 Tetrahymena Stock Center
Tetrahymena Stock Center
No Data fetched for Tetrahymena Stock Center
 Homologs
Homologs
No Data fetched for Homologs
 General Information
General Information
No Data fetched for General Information
 Associated Literature
Associated Literature
- Ref:34086947: Nabeel-Shah S, Garg J, Saettone A, Ashraf K, Lee H, Wahab S, Ahmed N, Fine J, Derynck J, Pu S, Ponce M, Marcon E, Zhang Z, Greenblatt JF, Pearlman RE, Lambert JP, Fillingham J (2021) Functional characterization of RebL1 highlights the evolutionary conservation of oncogenic activities of the RBBP4/7 orthologue in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic acids research ( ):
- Ref:14755052: Liu Y, Mochizuki K, Gorovsky MA (2004) Histone H3 lysine 9 methylation is required for DNA elimination in developing macronuclei in Tetrahymena. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101(6):1679-84
- Ref:14536085: Clements A, Poux AN, Lo WS, Pillus L, Berger SL, Marmorstein R (2003) Structural basis for histone and phosphohistone binding by the GCN5 histone acetyltransferase. Molecular cell 12(2):461-73
- Ref:12665578: Ren Q, Gorovsky MA (2003) The nonessential H2A N-terminal tail can function as an essential charge patch on the H2A.Z variant N-terminal tail. Molecular and cellular biology 23(8):2778-89
- Ref:12522258: Zilberman D, Cao X, Jacobsen SE (2003) ARGONAUTE4 control of locus-specific siRNA accumulation and DNA and histone methylation. Science (New York, N.Y.) 299(5607):716-9
- Ref:14661947: Poux AN, Marmorstein R (2003) Molecular basis for Gcn5/PCAF histone acetyltransferase selectivity for histone and nonhistone substrates. Biochemistry 42(49):14366-74
- Ref:12455963: Duharcourt S, Yao MC (2002) Role of histone deacetylation in developmentally programmed DNA rearrangements in Tetrahymena thermophila. Eukaryotic cell 1(2):293-303
- Ref:12351775: Jenuwein T (2002) Molecular biology. An RNA-guided pathway for the epigenome. Science (New York, N.Y.) 297(5590):2215-8
- Ref:12297044: Taverna SD, Coyne RS, Allis CD (2002) Methylation of histone h3 at lysine 9 targets programmed DNA elimination in tetrahymena. Cell 110(6):701-11
- Ref:12123289: Waterborg JH (2002) Dynamics of histone acetylation in vivo. A function for acetylation turnover? Biochemistry and cell biology = Biochimie et biologie cellulaire 80(3):363-78
- Ref:11891286: Shang Y, Song X, Bowen J, Corstanje R, Gao Y, Gaertig J, Gorovsky MA (2002) A robust inducible-repressible promoter greatly facilitates gene knockouts, conditional expression, and overexpression of homologous and heterologous genes in Tetrahymena thermophila. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99(6):3734-9
- Ref:11784863: Crosio C, Fimia GM, Loury R, Kimura M, Okano Y, Zhou H, Sen S, Allis CD, Sassone-Corsi P (2002) Mitotic phosphorylation of histone H3: spatio-temporal regulation by mammalian Aurora kinases. Molecular and cellular biology 22(3):874-85
- Ref:11972045: Dou Y, Gorovsky MA (2002) Regulation of transcription by H1 phosphorylation in Tetrahymena is position independent and requires clustered sites. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99(9):6142-6
- Ref:11135657: Tan S (2001) One HAT size fits all? Nature structural biology 8(1):8-10
- Ref:11467741: Green GR (2001) Phosphorylation of histone variant regions in chromatin: unlocking the linker? Biochemistry and cell biology = Biochimie et biologie cellulaire 79(3):275-87
- Ref:11751634: Briggs SD, Bryk M, Strahl BD, Cheung WL, Davie JK, Dent SY, Winston F, Allis CD (2001) Histone H3 lysine 4 methylation is mediated by Set1 and required for cell growth and rDNA silencing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes & development 15(24):3286-95
- Ref:10712850: Van Den Bussche RA, Hoofer SR, Drew CP, Ewing MS (2000) Characterization of histone H3/H4 gene region and phylogenetic affinity of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis based on H4 DNA sequence variation. Molecular phylogenetics and evolution 14(3):461-8
- Ref:11112280: Trievel RC, Li FY, Marmorstein R (2000) Application of a fluorescent histone acetyltransferase assay to probe the substrate specificity of the human p300/CBP-associated factor. Analytical biochemistry 287(2):319-28
- Ref:9396628: Fogel GB, Brunk CF (1997) Expression of Tetrahymena histone H4 in yeast. Biochimica et biophysica acta 1354(2):116-26
- Ref:8760889: Liu X, Gorovsky MA (1996) Cloning and characterization of the major histone H2A genes completes the cloning and sequencing of known histone genes of Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic acids research 24(15):3023-30
- Ref:1552842: Sadler LA, Brunk CF (1992) Phylogenetic relationships and unusual diversity in histone H4 proteins within the Tetrahymena pyriformis complex. Molecular biology and evolution 9(1):70-84
- Ref:1885002: Lin R, Cook RG, Allis CD (1991) Proteolytic removal of core histone amino termini and dephosphorylation of histone H1 correlate with the formation of condensed chromatin and transcriptional silencing during Tetrahymena macronuclear development. Genes & development 5(9):1601-10
- Ref:3360847: Richman R, Chicoine LG, Collini MP, Cook RG, Allis CD (1988) Micronuclei and the cytoplasm of growing Tetrahymena contain a histone acetylase activity which is highly specific for free histone H4. The Journal of cell biology 106(4):1017-26
- Ref:3822803: Horowitz S, Bowen JK, Bannon GA, Gorovsky MA (1987) Unusual features of transcribed and translated regions of the histone H4 gene family of Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic acids research 15(1):141-60
 Sequences
Sequences
>TTHERM_00189170(coding)
ATGGCCGGTGGAAAAGGTGGTAAAGGTATGGGTAAGGTCGGAGCCAAGAGACACTCCAGA
AAGTCCAATAAGGCTTCCATTGAAGGTATTACTAAGCCCGCTATCAGAAGATTAGCTAGA
AGAGGTGGTGTTAAGAGAATTTCCTCTTTCATTTATGATGACTCCAGACAAGTCTTGAAG
TCTTTCTTAGAAAACGTTGTTAGAGATGCTGTTACTTACACTGAACACGCCAGAAGAAAG
ACCGTCACTGCTATGGACGTCGTCTACGCTCTTAAGAGACAAGGCAGAACCCTCTATGGT
TTCGGTGGTTGA>TTHERM_00189170(gene)
AAATAAATAATCTAATTAAAAATAACAATAAAAAAATAATAATCCAGCAAAAATGGCCGG
TGGAAAAGGTGGTAAAGGTATGGGTAAGGTCGGAGCCAAGAGACACTCCAGAAAGTCCAA
TAAGGCTTCCATTGAAGGTATTACTAAGCCCGCTATCAGAAGATTAGCTAGAAGAGGTGG
TGTTAAGAGAATTTCCTCTTTCATTTATGATGACTCCAGACAAGTCTTGAAGTCTTTCTT
AGAAAACGTTGTTAGAGATGCTGTTACTTACACTGAACACGCCAGAAGAAAGACCGTCAC
TGCTATGGACGTCGTCTACGCTCTTAAGAGACAAGGCAGAACCCTCTATGGTTTCGGTGG
TTGAAAAACTTAAACTAACAAATAATAATCCAAAATACTCAAATACAAATATACTCATAT
AAAAAACAATTTAATTTATATATAAATTTTTTAGTGTCTGTGTATAATTACATTCATTAA
CTATTGTACATCGAGTTTAAAGTGTTTCACTATTCAAAATTCAATATTTTCTTCTTTCCA
ACTAAATCTTTTCAATCATTTCGTCTTAAACATAAAATCATTCAAATAAACAAACCAAAA
TCATACCTCAATCCATTCATTTTAAAATAACCAATTTTCCTTCGCCTTTTTTCGTTATTA
ATAAGCATAAACTTTTCCCCATAGTATGTTTAAATACAAATATTTATTTAATAGACCGTT
TACTTTATATTAATTATTAAGGTTGCTATATAATTCAATTCACTTACTTGCTTATTTATT
ATCATAA>TTHERM_00189170(protein)
MAGGKGGKGMGKVGAKRHSRKSNKASIEGITKPAIRRLARRGGVKRISSFIYDDSRQVLK
SFLENVVRDAVTYTEHARRKTVTAMDVVYALKRQGRTLYGFGG