Identifiers and Description
Identifiers and Description
Gene Model Identifier
TTHERM_00316500Standard Name
HTA2 (Histone h Two A 2)Aliases
H2A.2 | H2A2 | PreTt20961 | 31.m00263 | 3687.m00065Description
HTA2 histone H2B.1; Histone H2A; one of the four histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) that comprise the nucleosome core; one of two major histone H2A genes (with HTA1); knockout viable, but double knockout with HTA1 inviable; Histone H2AGenome Browser (Macronucleus)
Genome Browser (Micronucleus)
 External Links
External Links
 Gene Ontology Annotations
Gene Ontology Annotations
Cellular Component
- macronucleus (TAS) | GO:0031039
- micronucleus (NAS) | GO:0031040
- nucleosome (ISS) | GO:0000786
- nucleus (ISS) | GO:0005634
- subrhabdomeral cisterna (IEA) | GO:0016029
Molecular Function
- 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone binding (IEA) | GO:1903880
- 2-keto-3-deoxy-L-rhamnonate aldolase activity (IEA) | GO:0106099
- DNA binding (ISS) | GO:0003677
- ferric enterobactin:proton symporter activity (IEA) | GO:0015345
- lanosterol synthase activity (IEA) | GO:0000250
- mitochondrial single subunit type RNA polymerase activity (IEA) | GO:0001065
- obsolete sodium-transporting two-sector ATPase activity (IEA) | GO:0015443
- obsolete zinc, iron permease activity (IEA) | GO:0015342
- phosphatidylserine decarboxylase activity (IEA) | GO:0004609
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (ATP) activity (IEA) | GO:0004612
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity (IEA) | GO:0004611
- siderophore-iron transmembrane transporter activity (IEA) | GO:0015343
- type 4 neuropeptide Y receptor binding (IEA) | GO:0031844
Biological Process
- cellular response to homocysteine (IEA) | GO:1905375
- coenzyme A biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0015937
- heme A biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006784
- heme biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006783
- inactivation of recombination (HML) (IEA) | GO:0007537
- induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals (IEA) | GO:0008624
- lung connective tissue development (IEA) | GO:0060427
- lung epithelium development (IEA) | GO:0060428
- lung saccule development (IEA) | GO:0060430
- negative regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902647
- negative regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902642
- negative regulation of cellular glucuronidation (IEA) | GO:2001030
- negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response (IEA) | GO:1903898
- neutral lipid metabolic process (IEA) | GO:0006638
- nucleosome assembly (ISS) | GO:0006334
- obsolete aging (IEA) | GO:0007568
- obsolete extracellular carbohydrate transport (IEA) | GO:0006859
- obsolete regulation of histone H3-K27 methylation (IEA) | GO:0061085
- ommochrome biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006727
- plant-type cell wall modification (IEA) | GO:0009827
- positive regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902643
- positive regulation of dendrite extension (IEA) | GO:1903861
- positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining (IEA) | GO:2001034
- positive regulation of oxidative phosphorylation (IEA) | GO:1903862
- positive regulation of phospholipid translocation (IEA) | GO:0061092
- primary lung bud formation (IEA) | GO:0060431
- propan-2-ol biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902640
- protein localization to old growing cell tip (IEA) | GO:1903858
- pyrimidine nucleotide salvage (IEA) | GO:0032262
- regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902646
- regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902641
- regulation of cytokinin dehydrogenase activity (IEA) | GO:1903856
- regulation of ecdysteroid secretion (IEA) | GO:0007555
- regulation of gastric motility (IEA) | GO:1905333
- regulation of phosphorus utilization (IEA) | GO:0006795
- regulation of plant epidermal cell differentiation (IEA) | GO:1903888
- regulation of RNA binding transcription factor activity (IEA) | GO:1905255
- sesquiterpenoid biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0016106
- sperm aster formation (IEA) | GO:0035044
- sperm DNA decondensation (IEA) | GO:0035041
- synaptic vesicle priming (IEA) | GO:0016082
- tertiary alcohol biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902645
- transcription by RNA polymerase V (IEA) | GO:0001060
- tRNA import into mitochondrion (IEA) | GO:0016031
 Domains
Domains
 Gene Expression Profile
Gene Expression Profile
 Vegetative Cell Cycle (Zhang et al.,
2023)
Vegetative Cell Cycle (Zhang et al.,
2023)
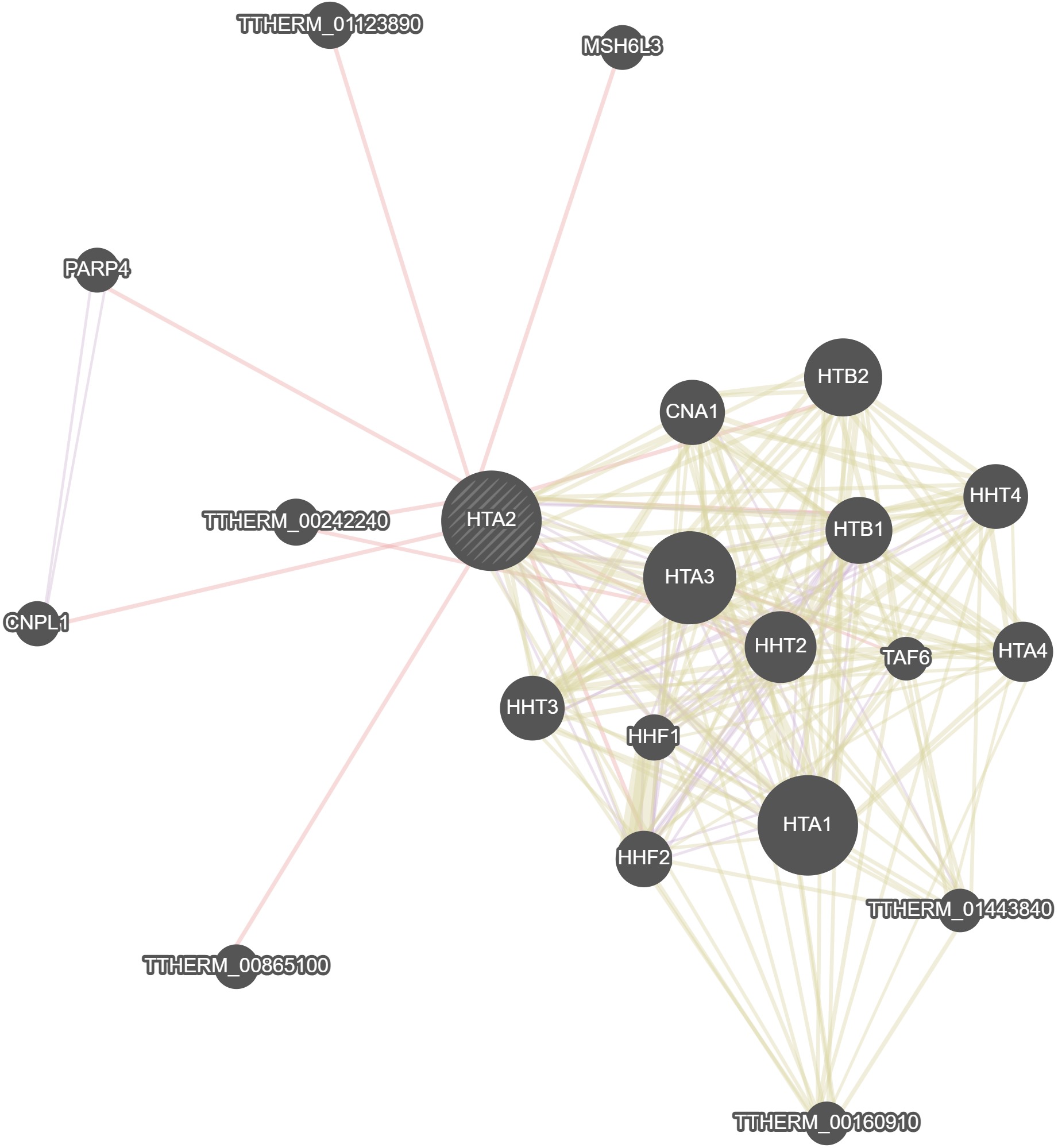
 GeneMania
GeneMania
 Tetrahymena Stock Center
Tetrahymena Stock Center
 Homologs
Homologs
No Data fetched for Homologs
 General Information
General Information
No Data fetched for General Information
 Associated Literature
Associated Literature
- Ref:12665578: Ren Q, Gorovsky MA (2003) The nonessential H2A N-terminal tail can function as an essential charge patch on the H2A.Z variant N-terminal tail. Molecular and cellular biology 23(8):2778-89
- Ref:11000274: Jackson JD, Gorovsky MA (2000) Histone H2A.Z has a conserved function that is distinct from that of the major H2A sequence variants. Nucleic acids research 28(19):3811-6
- Ref:10385122: Clarkson MJ, Wells JR, Gibson F, Saint R, Tremethick DJ (1999) Regions of variant histone His2AvD required for Drosophila development. Nature 399(6737):694-7
- Ref:8760889: Liu X, Gorovsky MA (1996) Cloning and characterization of the major histone H2A genes completes the cloning and sequencing of known histone genes of Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic acids research 24(15):3023-30
- Ref:8649398: Liu X, Bowen J, Gorovsky MA (1996) Either of the major H2A genes but not an evolutionarily conserved H2A.F/Z variant of Tetrahymena thermophila can function as the sole H2A gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular and cellular biology 16(6):2878-87
- Ref:8754831: Liu X, Li B, GorovskyMA (1996) Essential and nonessential histone H2A variants in Tetrahymena thermophila. Molecular and cellular biology 16(8):4305-11
- Ref:8177745: Liu X, Gorovsky MA (1993) Mapping the 5' and 3' ends of Tetrahymena thermophila mRNAs using RNA ligase mediated amplification of cDNA ends (RLM-RACE). Nucleic acids research 21(21):4954-60
- Ref:2587254: Mannironi C, Bonner WM, Hatch CL (1989) H2A.X. a histone isoprotein with a conserved C-terminal sequence, is encoded by a novel mRNA with both DNA replication type and polyA 3' processing signals. Nucleic acids research 17(22):9113-26
- Ref:3131141: Brandt WF, de Andrade Rodrigues J, von Holt C (1988) The amino acid sequence of wheat histone H2B(2). A core histone with a novel repetitive N-terminal extension. European journal of biochemistry 173(3):547-54
- Ref:6706903: Fusauchi Y, Iwai K (1984) Tetrahymena histone H2A. Acetylation in the N-terminal sequence and phosphorylation in the C-terminal sequence. Journal of biochemistry 95(1):147-54
- Ref:6885734: Fusauchi Y, Iwai K (1983) Tetrahymena histone H2A. Isolation and two variant sequences. Journal of biochemistry 93(6):1487-97
 Sequences
Sequences
>TTHERM_00316500(coding)
ATGAGCACAACTGGTAAAGGAGGTAAAGCTAAAGGTAAAACCGCTTCATCCAAGCAAGTT
TCTAGATCCGCTAGAGCTGGTCTTTAATTCCCCGTTGGTAGAATTTCCAGATTCTTGAAG
AACGGTAGATACAGTGAAAGAATCGGTACTGGTGCCCCCGTCTACTTGGCCGCTGTCTTA
GAATATTTGGCTGCTGAAGTTCTCGAATTGGCTGGTAACGCTGCTAAGGACAACAAGAAG
ACCAGAATTGTCCCCAGACATATTTTATTAGCTATCAGAAATGATGAAGAATTAAATAAA
CTCATGGCCAACACAACTATTGCTGATGGTGGTGTCTTACCCAACATCAACCCCATGCTT
CTTCCTTCTAAGACAAAGAAGTCCACTGAACCTGAACATTGA>TTHERM_00316500(gene)
AGGATTCTTCAAATTAATATAATTCAAAAACAAATAAAAATTAACAATCAATAAAAAAAG
AGATAATAATAACGATGAGCACAACTGGTAAAGGAGGTAAAGCTAAAGGTAAAACCGCTT
CATCCAAGCAAGTTTCTAGATCCGCTAGAGCTGGTCTTTAATTCCCCGTTGGTAGAATTT
CCAGATTCTTGAAGAACGGTAGATACAGTGAAAGAATCGGTACTGGTGCCCCCGTCTACT
TGGCCGCTGTCTTAGAATATTTGGCTGCTGAAGTTCTCGAATTGGCTGGTAACGCTGCTA
AGGACAACAAGAAGACCAGAATTGTCCCCAGACATATTTTATTAGCTATCAGAAATGATG
AAGAATTAAATAAACTCATGGCCAACACAACTATTGCTGATGGTGGTGTCTTACCCAACA
TCAACCCCATGCTTCTTCCTTCTAAGACAAAGAAGTCCACTGAACCTGAACATTGATTAA
TTGAAATTAAAACCTATACAAAAAAACTTACTTAATTTATAAACATATATATACTTTTTT
GTAAAATAGAGTTTGTGTGTATTCTTTCTAATTAAGCATTTCTAAGCTAATTAGTTAG>TTHERM_00316500(protein)
MSTTGKGGKAKGKTASSKQVSRSARAGLQFPVGRISRFLKNGRYSERIGTGAPVYLAAVL
EYLAAEVLELAGNAAKDNKKTRIVPRHILLAIRNDEELNKLMANTTIADGGVLPNINPML
LPSKTKKSTEPEH