Identifiers and Description
Identifiers and Description
Gene Model Identifier
TTHERM_01190440Standard Name
HOP3 (HOP2 (HOmologous Pairing 2) paralog 3)Aliases
PreTt14763 | 268.m00039 | HOP2B | HOPP2Description
HOP3 HOPP2 TBP1 interacting protein; Ubiquitously expressed paralog of meiotically expressed gene HOP2 (TTHERM_00794620); essential for vegetative growth; Ubiquitously expressed paralog of meiotically expressed gene HOP2 (TTHERM_00794620); essential for vegetative growth; Homologous-pairing protein 2, winged helix domainGenome Browser (Macronucleus)
Genome Browser (Micronucleus)
 External Links
External Links
 Gene Ontology Annotations
Gene Ontology Annotations
Cellular Component
- chloroplast ribosome (IEA) | GO:0043253
- ionotropic glutamate receptor complex (IEA) | GO:0008328
- obsolete ectoplasm (IEA) | GO:0043265
- omegasome (IEA) | GO:1990462
- subrhabdomeral cisterna (IEA) | GO:0016029
Molecular Function
- [citrate (pro-3S)-lyase] ligase activity (IEA) | GO:0008771
- 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone binding (IEA) | GO:1903880
- 2-octaprenyl-6-methoxyphenol hydroxylase activity (IEA) | GO:0008681
- 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase activity (IEA) | GO:0008691
- 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase activity (IEA) | GO:0008413
- alkene binding (IEA) | GO:0072328
- ferric triacetylfusarinine C:proton symporter activity (IEA) | GO:0015346
- lanosterol synthase activity (IEA) | GO:0000250
- metarhodopsin binding (IEA) | GO:0016030
- mitochondrial single subunit type RNA polymerase activity (IEA) | GO:0001065
- O-phospho-L-serine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity (IEA) | GO:0004648
- obsolete calcium-dependent secreted phospholipase A2 activity (IEA) | GO:0004625
- obsolete sodium-transporting two-sector ATPase activity (IEA) | GO:0015443
- obsolete X-His dipeptidase activity (IEA) | GO:0008769
- obsolete zinc, iron permease activity (IEA) | GO:0015342
- phosphatidylserine decarboxylase activity (IEA) | GO:0004609
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (ATP) activity (IEA) | GO:0004612
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity (IEA) | GO:0004611
- poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase activity (IEA) | GO:0004649
- regulatory region RNA binding (IEA) | GO:0001069
- siderophore uptake transmembrane transporter activity (IEA) | GO:0015344
- Swi5-Sfr1 complex binding (IEA) | GO:1905334
- transcription regulatory region RNA binding (IEA) | GO:0001068
- type 4 neuropeptide Y receptor binding (IEA) | GO:0031844
- UDP-galactopyranose mutase activity (IEA) | GO:0008767
Biological Process
- 3-keto-sphinganine metabolic process (IEA) | GO:0006666
- cell wall modification involved in fruit ripening (IEA) | GO:0009829
- coenzyme A biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0015937
- common myeloid progenitor cell proliferation (IEA) | GO:0035726
- epithelium development (IEA) | GO:0060429
- heme A biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006784
- heme biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006783
- immunoglobulin heavy chain V-D-J recombination (IEA) | GO:0071707
- induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals (IEA) | GO:0008624
- lung connective tissue development (IEA) | GO:0060427
- lung pattern specification process (IEA) | GO:0060432
- lung saccule development (IEA) | GO:0060430
- negative regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902647
- negative regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902642
- negative regulation of complement-dependent cytotoxicity (IEA) | GO:1903660
- negative regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining (IEA) | GO:2001033
- negative regulation of epithelial cell-cell adhesion involved in epithelium migration (IEA) | GO:1903682
- negative regulation of interleukin-4-mediated signaling pathway (IEA) | GO:1902215
- negative regulation of mRNA binding (IEA) | GO:1904572
- negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response (IEA) | GO:1903898
- negative regulation of protein localization to presynapse (IEA) | GO:1905385
- neutral lipid metabolic process (IEA) | GO:0006638
- Notch signaling pathway involved in negative regulation of venous endothelial cell fate commitment (IEA) | GO:2000796
- obsolete age dependent accumulation of genetic damage (IEA) | GO:0007570
- obsolete aging (IEA) | GO:0007568
- obsolete extracellular carbohydrate transport (IEA) | GO:0006859
- obsolete negative regulation of cytochrome-c oxidase activity (IEA) | GO:1905376
- obsolete pathogen-associated molecular pattern dependent induction by organism of symbiont innate immunity (IEA) | GO:0052498
- obsolete perturbation of host protein kinase-mediated signal transduction (IEA) | GO:0075130
- obsolete regulation of histone H3-K27 methylation (IEA) | GO:0061085
- obsolete regulation of nucleic acid-templated transcription (IEA) | GO:1903506
- obsolete reproduction (IEA) | GO:0000003
- obsolete response to lipoic acid (IEA) | GO:1990479
- obsolete response to long exposure to lithium ion (IEA) | GO:0043460
- obsolete sodium/potassium transport (IEA) | GO:0006815
- ommochrome biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006727
- plant-type cell wall cellulose metabolic process (IEA) | GO:0052541
- plant-type cell wall modification (IEA) | GO:0009827
- positive regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902643
- positive regulation of dendrite extension (IEA) | GO:1903861
- positive regulation of interleukin-4-mediated signaling pathway (IEA) | GO:1902216
- positive regulation of oxidative phosphorylation (IEA) | GO:1903862
- positive regulation of phospholipid translocation (IEA) | GO:0061092
- positive regulation of response to water deprivation (IEA) | GO:1902584
- pronuclear fusion (IEA) | GO:0007344
- propan-2-ol biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902640
- protein localization to old growing cell tip (IEA) | GO:1903858
- prothoracic disc morphogenesis (IEA) | GO:0007470
- pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0006221
- regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902646
- regulation of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate catabolic process (IEA) | GO:1902641
- regulation of cellular glucuronidation (IEA) | GO:2001029
- regulation of complement-dependent cytotoxicity (IEA) | GO:1903659
- regulation of cytokinin dehydrogenase activity (IEA) | GO:1903856
- regulation of germ cell proliferation (IEA) | GO:1905936
- regulation of phosphorus utilization (IEA) | GO:0006795
- regulation of plant epidermal cell differentiation (IEA) | GO:1903888
- response to polyamine macromolecule (IEA) | GO:1904583
- response to singlet oxygen (IEA) | GO:0000304
- sperm aster formation (IEA) | GO:0035044
- sperm DNA decondensation (IEA) | GO:0035041
- stilbene biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:0009811
- synaptic vesicle docking (IEA) | GO:0016081
- tertiary alcohol biosynthetic process (IEA) | GO:1902645
- transcription by RNA polymerase V (IEA) | GO:0001060
- triterpenoid catabolic process (IEA) | GO:0016105
- visceral muscle development (IEA) | GO:0007522
- vulval cell fate determination (IEA) | GO:0072326
- vulval cell fate specification (IEA) | GO:0072327
 Domains
Domains
- ( PF07106 ) TBPIP/Hop2 winged helix domain
 Gene Expression Profile
Gene Expression Profile
 Vegetative Cell Cycle (Zhang et al.,
2023)
Vegetative Cell Cycle (Zhang et al.,
2023)
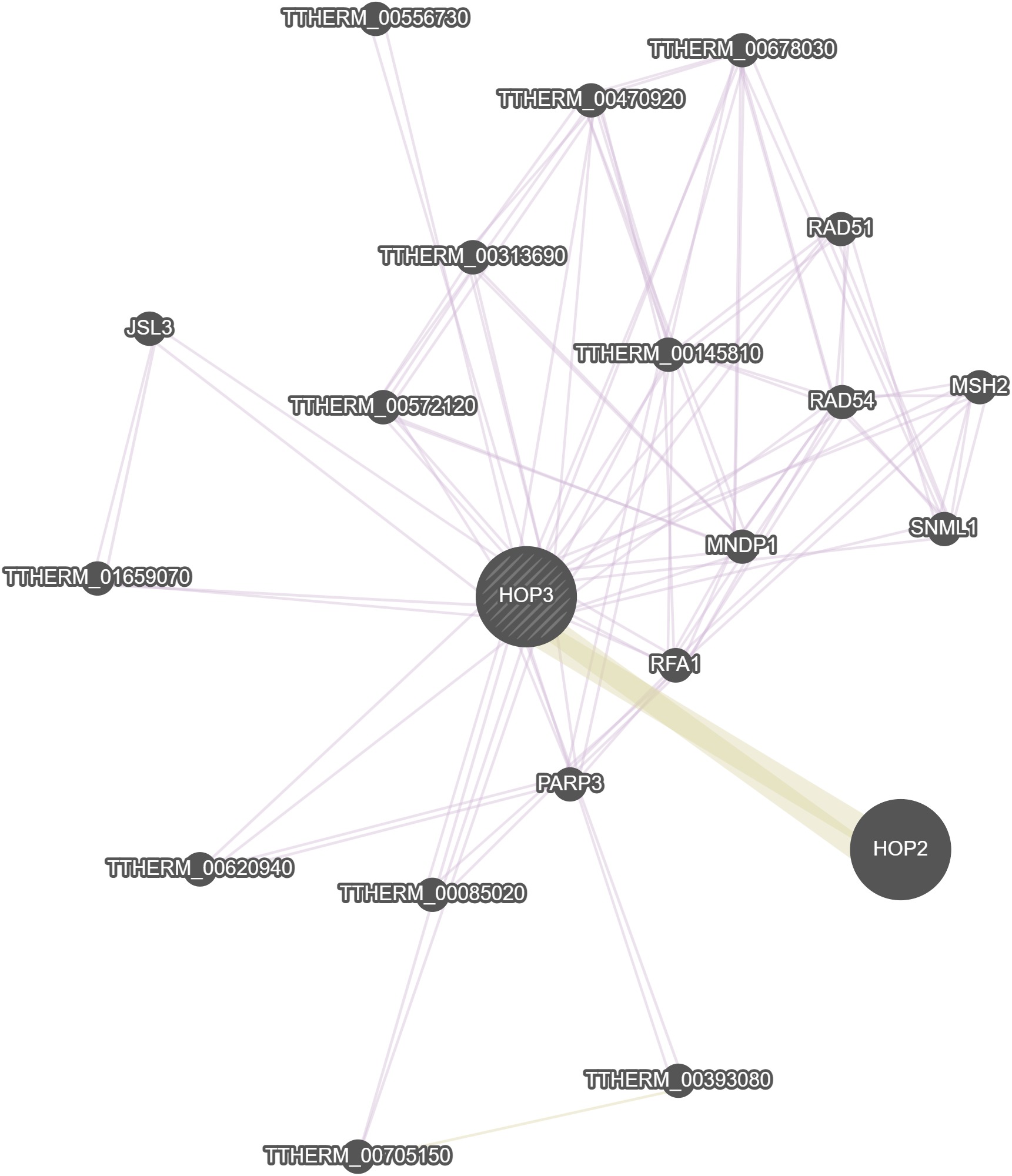
 GeneMania
GeneMania
 Tetrahymena Stock Center
Tetrahymena Stock Center
No Data fetched for Tetrahymena Stock Center
 Homologs
Homologs
No Data fetched for Homologs
 General Information
General Information
No. Gene Name(s) Paragraph Text 2260 MND1, MNDP1, HOP3 Hop2 and Mnd1 are meiosis-specific proteins that function in a complex in budding yeast. Their general architecture is strikingly similar, and therefore they are potentially homologous protein families. The Hop2-Mnd1 system seems to have undergone duplication in the evolutionary history of Tetrahymena, because both protein families are represented by two homologs with distinct expression patterns in this species. Just as for HOP2 (meiotic) and HOPP2 (ubiquitous), there is a meiotic (MND1)and a ubiquitously expressed (MNDP1) version, which raises the possibility that a meiotic and a ubiquitous Mnd1p-Hop2p complex exists. 2261 MND1, MNDP1, HOP3 Hop2 and Mnd1 are meiosis-specific proteins that function in a complex in budding yeast. Their general architecture is strikingly similar, and therefore they are potentially homologous protein families. The Hop2-Mnd1 system seems to have undergone duplication in the evolutionary history of Tetrahymena, because both protein families are represented by two homologs with distinct expression patterns in this species. Just as for HOP2 (meiotic) and HOPP2 (ubiquitous), there is a meiotic (MND1)and a ubiquitously expressed (MNDP1) version, which raises the possibility that a meiotic and a ubiquitous Mnd1p-Hop2p complex exists. 2262 MND1, MNDP1, HOP3 Hop2 and Mnd1 are meiosis-specific proteins that function in a complex in budding yeast. Their general architecture is strikingly similar, and therefore they are potentially homologous protein families. The Hop2-Mnd1 system seems to have undergone duplication in the evolutionary history of Tetrahymena, because both protein families are represented by two homologs with distinct expression patterns in this species. Just as for HOP2 (meiotic) and HOPP2 (ubiquitous), there is a meiotic (MND1)and a ubiquitously expressed (MNDP1) version, which raises the possibility that a meiotic and a ubiquitous Mnd1p-Hop2p complex exists. 2263 MND1, MNDP1, HOP3 Hop2 and Mnd1 are meiosis-specific proteins that function in a complex in budding yeast. Their general architecture is strikingly similar, and therefore they are potentially homologous protein families. The Hop2-Mnd1 system seems to have undergone duplication in the evolutionary history of Tetrahymena, because both protein families are represented by two homologs with distinct expression patterns in this species. Just as for HOP2 (meiotic) and HOPP2 (ubiquitous), there is a meiotic (MND1)and a ubiquitously expressed (MNDP1) version, which raises the possibility that a meiotic and a ubiquitous Mnd1p-Hop2p complex exists. 2223 HOP3 HOP2B is a homolog of budding yeast HOmologous Pairing 2. It is essential for vegetative growth. HOP2B has a meiosis-specific paralog in Tetrahymena (HOP2, HOP2A, TTHERM_00794620) which is the yeast HOP2 ortholog.
 Associated Literature
Associated Literature
- Ref:18522989: Mochizuki K, Novatchkova M, Loidl J (2008) DNA double-strand breaks, but not crossovers, are required for the reorganization of meiotic nuclei in Tetrahymena. Journal of cell science 121(Pt 13):2148-58
 Sequences
Sequences
>TTHERM_01190440(coding)
ATGAGTTAAGTTGAAGAAAAAGTTGATGTTGAAGAGGGTGCTCAAGAAAACGATCAAGCT
GAAGATACAGGAAGAAGAAGATCTACAAGAGCAAGAGCTCCTCCTGCACCTACTGCTCCT
GCTGCTAAGAAAGATCCTAAGGCAGCAAAGGGAGCTAAGAAGGGCGCAGCTAAAAAAGAT
CCTAAATAGAAAAAAGGAGCAAAAAAGAAAGGATCTGATGATGAAGATTCAGACATTGAA
ATTATTGAAGACAAGCCAGAAAATATGGATGACGAAGAAGAAGAAATTAAAGAAAAAAAA
GAAACAAAAGAAAAAAAAGATGATGAATTAGATGAAGAAGATGAAATTGAAGAAGAACCT
TCTGAAGATGACGATGATGAGGAAGATGAATTTGATGAAAAGCCAAAAAAGAAAGGAAAA
GGTGCTGCTAAATCTGCACCCGCTGCTAAAAAAGGTAAGGCAGCTGAAAAGCCTGAAAAG
AAGGCTCCTGCTACTAAAGCTCCTGCAGCCAAAGGCAAAAAGAAATCTAAAGAAAGCGAT
GATGAAGACGACTTTAATGATGATAGTGAAGAGGCTAAACCAAAGGGAAAAGGTGGAGCT
GCTAAAAAGGGTGCTCCTGCTAAGAAGGGAAAAAAAGATGAAGATGATGGAGGCACTGTT
GATGATGATACTGTACTTGAATATATGAAGAAAGCTAATAGACCATATTCTTTGATTAAT
ATTTGTGATAATTTACATGGAAAAATTAAGAAGACCGCTTTATAGAAAATGCTCGATGGG
TTGGTCAGTAAGAATAAATTGACTTGCAAAGAGTTTGGTAAAGCTAAAATTTATCTCATG
AATTAAGATTTGTTGCCATAGGTTGATAAATCAGAGCTAGAATAAATGCAAAATGATTTG
AATGAAAAAAGAGTTTACTTGAGAGAAATTGGTGAAGAAATCAAAGAACTTACTAAAAAA
ATAGCCACTTATAATAAATAATTAACCAATGCTTAAATTTAAGAAGAAATTGTAAAGAAC
GAAAAAATGATTAAGTAACTAGAAGATAAAATGCATTTCTATTAAAGTGATAAATTCGTT
TAAGCATCAGAATCCGATGTTAAGAAGCACGAAGAAGCATATCAAAAAATGGAGAAAGAA
TACAAGAGACGTAGAAGAATGTGTAAGGATGGTATTGGTCAAATAGCTGAAGGTATGAAT
AAAAAGCTATCAGAAGTATAAGAATTGATTGGAATAGAAGAGGAAGATGAGTGA>TTHERM_01190440(gene)
TATATCAGATATATTTGAACTCAACAGTCATAAATAGAATGAAAAGGATATTTTTTAATT
TAAAATCAATTGGATTAATAGATTATAATTTTTGTGCGCTCAAATTATATTATTTTAAGT
AAAAATAATAATAAATCAAAAACAATTAGTAAATATAATTTTTTGCCTTTAATAATTTAG
TATATCTATCTATCTATCAGTGCTAATTACAAGCAATACATAAATAGCTACATAATCTAT
AATTAATAAATAAATCAACAAATAATATCAAACATAACCAACTAATTATTCCATAGTTTG
AATTGTTAATACAAAGATGAGTTAAGTTGAAGAAAAAGTTGATGTTGAAGAGGGTGCTCA
AGAAAACGATCAAGCTGAAGATACAGGAAGAAGAAGATCTACAAGAGCAAGAGCTCCTCC
TGCACCTACTGCTCCTGCTGCTAAGAAAGATCCTAAGGCAGCAAAGGGAGCTAAGAAGGG
CGCAGCTAAAAAAGATCCTAAATAGAAAAAAGGAGCAAAAAAGAAAGGATCTGATGATGA
AGATTCAGACATTGAAATTATTGAAGACAAGCCAGAAAATATGGATGACGAAGAAGAAGA
AATTAAAGAAAAAAAAGAAACAAAAGAAAAAAAAGATGATGAATTAGATGAAGAAGATGA
AATTGAAGAAGAACCTTCTGAAGATGACGATGATGAGGAAGATGAATTTGATGAAAAGCC
AAAAAAGAAAGGAAAAGGTGCTGCTAAATCTGCACCCGCTGCTAAAAAAGGTAAGGCAGC
TGAAAAGCCTGAAAAGAAGGCTCCTGCTACTAAAGCTCCTGCAGCCAAAGGCAAAAAGAA
ATCTAAAGAAAGCGATGATGAAGACGACTTTAATGATGATAGTGAAGAGGCTAAACCAAA
GGGAAAAGGTGGAGCTGCTAAAAAGGGTGCTCCTGCTAAGAAGGGAAAAAAAGATGAAGA
TGATGGAGGCACTGTTGATGATGATACTGTACTTGAATATATGAAGAAAGCTAATAGACC
ATATTCTTTGATTAATATTTGTGATAATTTACATGGAAAAATTAAGAAGACCGCTTTATA
GAAAATGCTCGATGGGTTGGTCAGTAAGAATAAATTGACTTGCAAAGAGTTTGGTAAAGC
TAAAATTTATCTCATGAATTAAGATTTGTTGCCATAGGTTGATAAATCAGAGCTAGAATA
AATGCAAAATGATTTGAATGAAAAAAGAGTTTACTTGAGAGAAATTGGTGAAGAAATCAA
AGAACTTACTAAAAAAATAGCCACTTATAATAAATAATTAACCAATGCTTAAATTTAAGA
AGAAATTGTAAAGAACGAAAAAATGATTAAGTAACTAGAAGATAAAATGCATTTCTATTA
AAGTGATAAATTCGTTTAAGCATCAGAATCCGATGTTAAGAAGCACGAAGAAGCATATCA
AAAAATGGAGAAAGAATACAAGAGACGTAGAAGAATGTGTAAGGATGGTATTGGTCAAAT
AGCTGAAGGTATGAATAAAAAGCTATCAGAAGTATAAGAATTGATTGGAATAGAAGAGGA
AGATGAGTGAGCGAGAAAAAGCTTTATTACTCTAAAATGTTAAAAAATAAACAAATTAGG
CAAATTGATGAATTGAATATAAAATACTCTATTAATAATTAAGTTACACACTATTATAAT
ATTACAAATTTAACTAACATATAATCAATACATCATATAAATTTCATTGTATGGTTGATT
TATATATCTGTCCTTAATTTCTTTTGTTCATTTTTCCTTAAGCGATTATAATTAATA>TTHERM_01190440(protein)
MSQVEEKVDVEEGAQENDQAEDTGRRRSTRARAPPAPTAPAAKKDPKAAKGAKKGAAKKD
PKQKKGAKKKGSDDEDSDIEIIEDKPENMDDEEEEIKEKKETKEKKDDELDEEDEIEEEP
SEDDDDEEDEFDEKPKKKGKGAAKSAPAAKKGKAAEKPEKKAPATKAPAAKGKKKSKESD
DEDDFNDDSEEAKPKGKGGAAKKGAPAKKGKKDEDDGGTVDDDTVLEYMKKANRPYSLIN
ICDNLHGKIKKTALQKMLDGLVSKNKLTCKEFGKAKIYLMNQDLLPQVDKSELEQMQNDL
NEKRVYLREIGEEIKELTKKIATYNKQLTNAQIQEEIVKNEKMIKQLEDKMHFYQSDKFV
QASESDVKKHEEAYQKMEKEYKRRRRMCKDGIGQIAEGMNKKLSEVQELIGIEEEDE